Boyle's Law states that the volume of a sample of gas is inversely proportional to the pressure applied to the gas if the temperature is kept constant.
According to Boyle's Law:
P1 x V1 = constant
After the change in pressure and volume,
P2 x V2 = constant
Combine the two products:
P1 x V1 = P2 x V2
When any three of the four quantities in the equation are known, the fourth can be calculated. For example, if P1, V1 and P2 are known, the V2 can be solved by the following equation:
V2 = P1 x V1 / P2
The force exerted per unit area of surface, typical pressure units are ATM, mmHg and kPa.
The measurement of space taken by a substance, it is length cubed, typical units are L, mL and m3.
A measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample of matter, expressed in terms of units or degrees designated on a standard scale. Typical units are K, F and C.
The mass of the object divided by its volume. Typical units are g/mL and kg/m3.
The formula weight of a compound is the sum of all the atomic weights of the elements present in the formula of the compound. Some text also refers it to formula mass. Typical unit is g/mol.
Mass is the amount of a substance in grams, also called weight.
The constant that appears in the ideal gas equation (PV=nRT). It is usually expressed as 0.08206 L x atm/K x mol or 8.314 J/K x mol.
The number of moles of solute dissolved in one kilogram of solvent.
The number of moles of solute in one liter of solution.
With four quantities in P1V1=P2V2 equation, given any three, the forth one can be calculated based on the Boyle's Law.
In addition to the problem solving module, the "Show Work" is also displayed along with the solution to illustrate the step-by-step guide in how your problem has been solved.
This is one step process, enter the known data and press Calculate to output the unknowns.
1. Select Boyle's Law link from the front page or Bolye tab from the Gases module. The Input and Output screen appears.
2. In the Input area, enter the three known quantities with a proper significant figure. Select the units associated with the input.
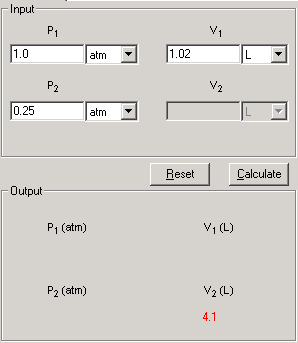
3. Click Calculate to output the answer.
4. The Show Work area on the right shows you step-by-step how your problem has been solved.
To start a new problem, click Reset. All Input fields will be cleared. Follow Step 1-3 again.